
The Future of Warfare
-

Vision
The Future of Warfare
-
The concept of warfare has been changing along with the development of weapons systems resulting from scientific and technological advances. The paradigm of war, in particular, has been shifting with the occurrence of industrial revolutions that have sparked and driven technological evolution. Here, we examine the future of warfare including its major forms that is expected based on technological progress.
- Changes in the Concept of Warfare Resulting from Industrial Revolutions

- Multi-domain Battlefield
With the development of science and technology, the military operations environment is becoming multidimensional and nonlinear. War will be fought in five dimensions, which include the traditional battlefields of land, sea, and air as well as cyberspace and space. War will not only be fought on the frontline formed with the enemy in one horizontal space; multiple battles will occur the same time on multidomain battlefields.
- Network-centric Environment
In multi-dimensional warfare, each element of combat will be connected to the network for sharing of information and command-control operations. The battle space will be a unit area, and categorizing them will become meaningless. In future warfare, sharing of the battle situation and real-time command and control will be possible based on the network, irrespective of the physical distance.
- Cyber Warfare
This relates to the act of securing information in cyberspace composed of computers and networks and defending and protecting streams of information against delays, damages, and paralysis caused by the enemy. Cyber attacks can paralyze a nation’ ability to engage in war, as they tend to affect all domains of society and all functions of a super-intelligent, super-connected nation. Hacking, computer viruses, etc. will continue to be utilized as a means of cyber warfare, and in response, intrusion prevention, cryptography, authentication, vaccine, and CERT (Computer Emergency Response Team) among other technologies developed for protection will continue to be developed and utilized, like as a relationship between spears and shields.
- Space Operations
In future warfare, space will be regarded as a new strategic base. This does not simply indicate an expansion of the physical space. It means there will be increased utilization of space surveillance, reconnaissance and communication assets, such as target detection, identification and tracking, and satellites for command, control and communication, and a growing need to secure space control assets for containment, delay, and disruption of the enemies’ development of space power. Furthermore, new space weapons systems are expected to emerge according to the understanding and capabilities of each country, and such includes space strike systems, space bombs, and space missiles. As such, space will play an increasingly important role in warfare..
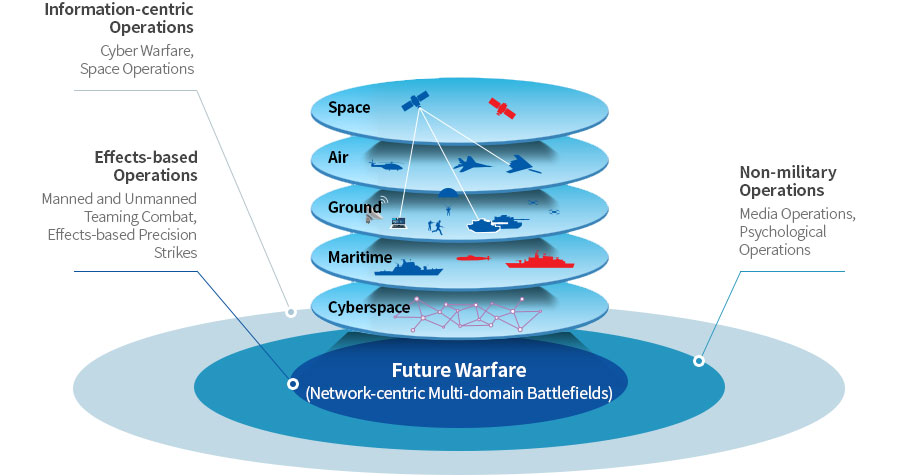
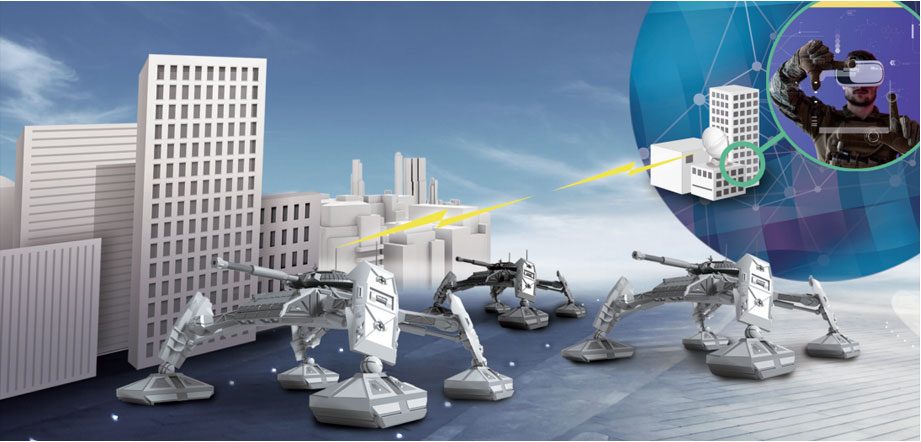
- Manned and Unmanned Teaming Combat
In warfare, robots will, on behalf of combatants, perform high-risk missions, such as removing land mines and explosives and CBR (Chemical, Biological and Radiological) decontamination. It is also expected that the machines will carry out combat support missions to destroy enemy targets in the distant future. Nevertheless, they will not be able to completely replace humans. That is, using robots for simple, repetitive, and dangerous tasks and ensuring collaboration with humans, who are capable of making quick calls and responses in sudden, unexpected situations, will be necessary to ultimately lead to victory.
- Effects-based Precision Strikes
In the past, wars were fought to destroy the enemy’s ability to fight war. However, in the future, the focus will be on minimizing collateral damage and achieving effects that are attainable. To this end, all targets that are deemed as threats will be detected and monitored, and the most appropriate means to eliminate the threat will be used.


United States
United States of America- Establishment of the Office of the Under Secretary of Defense for Research and Engineering (2018) - Expansion of technology investment in support of the Third Offset Strategy (TOS) - Responding to demands for innovative technology (game changers)
- Establishment of the Defense Innovation Unit (2018) - Introduction of innovative civilian technologies to the defense sector - Commercialization of defense research outcomes
- Appointment of Principal Directors for DoD's Modernization Priorities - Modernization Priorities: 5G, Artificial Intelligence, Autonomy, Biotechnology, Cyber, Directed Energy, FNC3 (Fully Networked Command, Control and Communications), Hypersonics, Microelectronics, Quantum Science, and Space.

United Kingdom
United Kingdom- Establishment of the Defense Innovation Initiative (2016) - Creation of a defense innovation fund of £800M (2017-2025)
France
France- Establishment of the Defense Innovation Agency (2018) - Annual Investment of €12B to integrate innovative defense technologies and state-of-the-art civilian technologies - Long-term innovation projects: Quantum Applications, High-speed Helicopters, Short-range Ultra High-speed Armaments, C2 (Command and Control) Clouds, Aircraft Carriers, etc.

Australia
Australia- Establishment of the Next Generation Technologies Fund (2016) - Investment of AUD 730M in defense science and technology by 2026 - Major Areas: Cyber, Quantum Technology, Hypersonic, Directed Energy, Space, Integrated ISR (Intelligence, Surveillance and Reconnaissance), Trusted Autonomous Systems, etc.
top
